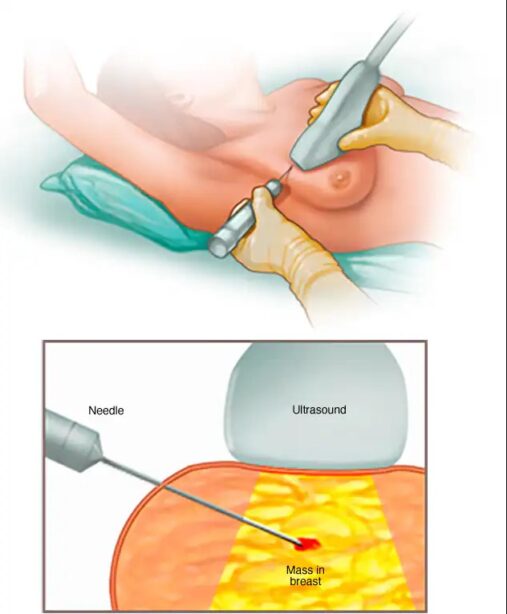
A Breast Biopsy is a procedure to remove a sample of breast tissue for testing. The tissue sample is sent to a lab, where doctors specializing in analyzing blood and body tissue (pathologists) examine and diagnose it.
A breast biopsy might be recommended if you have a suspicious area in your breast, such as a breast lump or other signs and symptoms of breast cancer. It can also investigate unusual findings on a mammogram, ultrasound, or other breast exam.
The results of a breast biopsy can show whether the area in question is breast cancer or if it’s not cancerous. The pathology report from the breast biopsy can help your doctor determine whether you need additional surgery or other treatment.
Why it’s done
Your doctor may recommend a breast biopsy if:
You or your doctor feel a lump or thickening in the breast, and your doctor suspects breast cancer
Your mammogram shows a suspicious area in your breast
An ultrasound scan or breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) reveals a suspicious finding
You have unusual nipple or areolar changes, including crusting, scaling, dimpling skin, or a bloody discharge
Risks
Risks associated with a breast biopsy include:
- Bruising and swelling of the breast
- Infection or bleeding at the biopsy site
- Altered breast appearance, depending on how much tissue is removed and how the breast heals
- Additional surgery or other treatment, depending on biopsy results
Contact your healthcare team if you develop a fever, if the biopsy site becomes red or warm, or if you have unusual drainage from the biopsy site. These can be signs of an infection that may require prompt treatment.