What is a CCT angiogram?
A computed tomography (CT) angiogram is a test to view blood vessels and tissues. During the test, your provider injects a dye highlighting your blood vessels and tissues. Then, your provider takes a CT scan, a specialized X-ray, to view the highlighted areas.
Why might I need a CCT angiogram?
The most common reason to have a CT angiogram is to see if you have narrowed or blocked coronary arteries. But your healthcare provider may use a CT angiogram to diagnose any condition involving your blood vessels, including:
- Aneurysms, irregular bulges or widening of your blood vessels.
- Atherosclerosis (fatty plaques that build inside blood vessels).
- Coronary Artery Disease
- Pulmonary Embolism
What is the difference between a CT angiogram and a traditional angiogram (or cardiac catheterization)?
CCT angiograms and traditional angiograms are both tests to view your blood vessels. CCT angiograms are less invasive than traditional angiograms.
With traditional angiography, your provider inserts a long, hollow tube (catheter) through a large blood vessel called an artery, usually in your groin or wrist. Then, the provider injects contrast dye through the catheter and uses X-ray fluoroscopy to image your coronary arteries (blood vessels).
With a CCT angiogram, your provider injects the contrast dye through an IV into your vein (intravenously). They usually insert the IV into a vein in your arm or hand.
Who performs a CT angiogram?
Typically, a radiologist performs this test. Radiologists are doctors who specialize in taking and interpreting imaging scans. If you have a CCTA coronary angiogram, a radiologist specializing in cardiovascular images performs the test.
TEST DETAILS
How do I prepare for a CCT angiogram?
Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions to prepare for a CT angiogram. You may have to stop certain medications, such as vasodilators (Viagra®, Levitra®), temporarily before the test.
Typically, you’ll stop eating around four hours before the test. You can drink water as usual.
If you’re having a coronary CCT angiogram, you must avoid caffeine within 12 hours of the test. Caffeine can increase your heart and make it more difficult to get a clear picture of your coronary arteries.
What should you expect on the day of the CT angiogram?
You usually have a CCT angiogram in an outpatient imaging facility or the radiology department at a hospital. When you arrive, you’ll change into a hospital gown. You’ll remove eyeglasses and all metal objects, such as jewelry, hairpins, or dentures that contain metal. If you have a pacemaker, joint replacement, or other metal implants in your body, you can usually still have a CCT angiogram because most implants are made of titanium. Tell your healthcare provider if you have a metal implant.
What to expect during a CT angiogram?
During a CT angiogram:
- A technician inserts an IV through your arm or hand. Contrast dye flows through the IV.
- For a coronary CT angiogram, the technician attaches sticky patches (electrodes) to your chest. The electrodes connect to a machine that records your heart rate and rhythm.
- You lie on a table that glides into a machine shaped like a doughnut (CT scanner).
- A technician operates the CT scanner from another room, taking images from several angles. They may instruct you to hold your breath for a few seconds to prevent chest movement during the scan.
The actual CT scan may only take a few seconds to minutes. With setup time, the procedure typically takes around an hour.
What to expect after a CT angiogram?
You can return home and resume usual activities the same day as a CT angiogram. Your provider will tell you to drink plenty of water to help flush the contrast dye out of your system.
RESULTS AND FOLLOW-UP
When should I know the results of the test?
Your provider typically reviews test results with you over several days or weeks. Depending on the test results, you may need follow-up exams. Or, if the test shows a risk of heart disease, your provider may discuss treatment options with you.
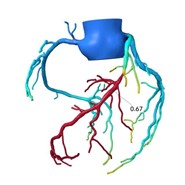
HeartFlow® Analysis
The Heart Flow pathway begins with a Coronary CTA. If the Physician sees a disease, the CTA images are sent to Heart Flow where A. I (Artificial Intelligence) algorithms computational fluid dynamics and train analysts to create a Heart Flow Analysis. This personal color-coded 3D model of a patient’s arteries provides functional information about each blockage.
Cleerly®Analysis
Cleerly uses proprietary and FDA-cleared machine learning algorithms to non-invasively measure atherosclerosis (plaque), stenosis, and likelihood of ischemia using coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) studies.
Our machine-learning AI generates a 3D model of the patient’s coronary arteries, identifies their lumen and vessel walls, and locates and measures stenoses while quantifying and categorizing plaque.1 Cleerly ISCHEMIA’s algorithm uses measurements based on invasive FFR data to determine the likelihood of vessel-level ischemia.2
These quantitative measurements are presented in a comprehensive report to support providers in efficient diagnosis and personalized patient treatment. Physicians can also review results in depth via our interactive web platform.