At ImageCare Radiology, we are proud to offer uterine artery embolization in New Jersey, providing an advanced women’s health and infertility treatment option for the management of symptoms caused by uterine fibroids. This minimally invasive procedure is a proven alternative to surgery, helping patients recover quicker with less discomfort.
What is Uterine Fibroid Embolization?
Uterine fibroid embolization is a non-surgical treatment aimed at reducing the symptoms of uterine fibroids, which are non-cancerous tumors originating from the muscular tissue of the uterus.
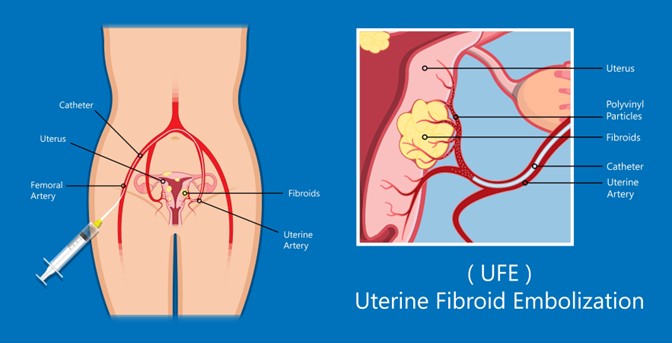
The procedure involves making a small incision to access the blood vessels, using advanced imaging to guide catheters, and then injecting tiny particles approximately the size of grains of sand into the arteries that supply blood to the fibroids. These particles block the blood flow to the fibroids, causing them to shrink and, over time, leading to an alleviation of symptoms.
The particles used in uterine fibroid embolization have been safely utilized in various medical treatments for many years. The procedure itself is performed by an interventional radiologist who specializes in minimally invasive, targeted treatments using imaging for guidance.
Who Would Need Uterine Fibroid Embolization?
A uterine artery embolization procedure is typically recommended for women experiencing significant symptoms from fibroids, such as:
- Severe pain or fullness in the lower abdomen
- Excessive menstrual bleeding leading to anemia
- Frequent urination due to bladder pressure
- Pain during intercourse
- Back or leg pain from nerves pressed by fibroids
Although fibroids are usually benign, their impact on quality of life can be profound. Uterine fibroid embolization offers a less invasive solution compared to traditional surgical approaches like hysterectomy or myomectomy, and it is an option even when fibroids are large or numerous.
Preparing for Uterine Fibroid Embolization
Understanding the risks and uterine artery embolization side effects and preparing for the procedure is critical. Possible complications can include, but are not limited to, minor risks like bleeding or infection at the puncture site, and more severe issues such as possible impacts on future fertility. Women might also experience post-embolization syndrome, which includes symptoms such as pain, fever, nausea, and fatigue. These symptoms are typically temporary and manageable with medications.
It’s essential for patients to discuss their full medical history and concerns with their healthcare provider to ensure uterine fibroid embolization is appropriate for their specific situation.
What Happens During Uterine Fibroid Embolization?
Uterine fibroid embolization is performed as an outpatient procedure at ImageCare Radiology. Depending on your condition and healthcare provider’s practices, the process may vary. However, it generally follows the steps below:
First, you will be asked to remove any jewelry or objects that may hinder the procedure and will be given a gown to wear. An IV line will then be started in your arm or hand, and antibiotic medicine may be given to you before the procedure. You will lie on your back on the procedure table, and a long, thin tube (catheter) will be inserted into your bladder to drain urine. During the procedure, medical staff will monitor your heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, and blood oxygen level.
The healthcare provider will clean the groin area with an antiseptic solution and insert a small tube (sheath) into your groin area. This will act as a guide for inserting the catheter into the arteries to be blocked off (embolized). The provider will inject contrast dye into the catheter to help find the artery to be blocked off. They will use X-rays to locate the blood vessels that supply blood to each fibroid. A tiny catheter will be put into the groin (femoral artery) and moved into the arteries that need to be blocked. Tiny particles will be injected into the blood vessels, and the provider will take more X-ray images to ensure that the arteries are blocked.
Some providers will use one groin site to treat both the left and right uterine arteries if needed, while others may use two groin sites. The sheath and catheter will be removed after the embolization is complete.
What Happens After Uterine Fibroid Embolization?
After a uterine fibroid embolization, medical staff will apply pressure on the groin insertion site for around 20 minutes to stop bleeding. You will then be taken to the recovery room where staff will monitor your blood pressure, pulse, and breathing while you lie flat for a few hours. Your recovery process will depend on the type of medicine used to help you relax. Once your vital signs are stable and alert, you will be sent home.
After the procedure, you may experience belly cramping and minor to moderate amounts of fluid draining from your vagina for several days. The nurse will check the sanitary pads to determine the amount of drainage. You may also receive pain medicine from a nurse or device connected to your IV line.
Your healthcare provider will encourage you to get out of bed once you have rested and your groin puncture site has been sealed. You should also do coughing and deep breathing exercises as instructed by your nurse. A few hours later, you may be given liquids to drink, and your diet may gradually change to more solid foods as you are able to eat them.
Once you are home, it is important to keep the groin incision clean and dry, adhering to specific bathing instructions from your healthcare provider. If adhesive strips are used, they should be kept dry and will usually fall off within a few days. You may experience aching at the incision site and in your abdominal and pelvic muscles, especially after standing for long periods. Take a pain reliever as recommended by your healthcare provider to ease soreness.
Your healthcare provider will likely advise walking and limited movement and tell you when you can return to work and resume normal activities. Be sure to include fiber and plenty of fluids in your diet to prevent constipation. Straining to have a bowel movement may cause problems, so your provider may recommend a mild laxative.
Refrain from using a douche or tampons or engaging in sex until your healthcare provider says it is safe to do so. Also, don’t return to work until your provider says it is okay. Notify your healthcare provider if you experience fever or chills, redness, swelling, bleeding, or other fluid drains from the incision site, increased pain around the incision site, abdominal pain, cramping, or swelling, or increased vaginal bleeding or passing of tissue or other drainage.
You will need to visit your healthcare provider for a follow-up visit, often 1 to 2 weeks after the procedure. At that time, the provider may schedule an ultrasound or MRI in 6 months to evaluate the effectiveness of the procedure. Your provider may also give you other instructions, depending on your situation.
Contact Us to Schedule a Uterine Fibroid Embolization Procedure
If you’re suffering from symptoms caused by uterine fibroids, contact ImageCare Radiology to learn more about uterine fibroid embolization and whether it’s the right option for you. Call us at (973) 810-8100 to schedule a consultation and take the first step toward improving your health and quality of life.